In today’s digital age, file sharing is commonplace, yet it can be challenging due to size restrictions on email and messaging platforms. For example, Gmail limits file attachments to 25 MB, and Outlook allows only 20 MB.
Luckily, numerous methods exist for sending large files, some of which we’ll explore below. While we’ve found the Commander One app to be highly effective, we’ll also review other options to help you share big files, whether long videos or entire media libraries.
Compressing large files for sending
Compressing files is crucial for efficient data transfer, particularly when dealing with large files or email size restrictions. Most operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Ubuntu, come with built-in archiving features. For instance, on macOS, you can control-click on a file you want to zip and choose “Compress” from the menu.
Additionally, there are third-party file compression software and apps like Commander One, WinRAR, and 7-Zip. Compared to native solutions, these utilities offer more advanced functionality and boast wider format support. The compressed files can then be easily attached to emails and forwarded to recipients.
How to compress files via Commander One
Commander One is a versatile dual-pane file manager equipped with robust archiving capabilities. It allows users to compress files into ZIP, 7Z, TXZ, and other formats. You can even copy, move, edit, and search directly in the archive, without unpacking it first.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on compressing large files with Commander One:
Download and install the app on your Mac.
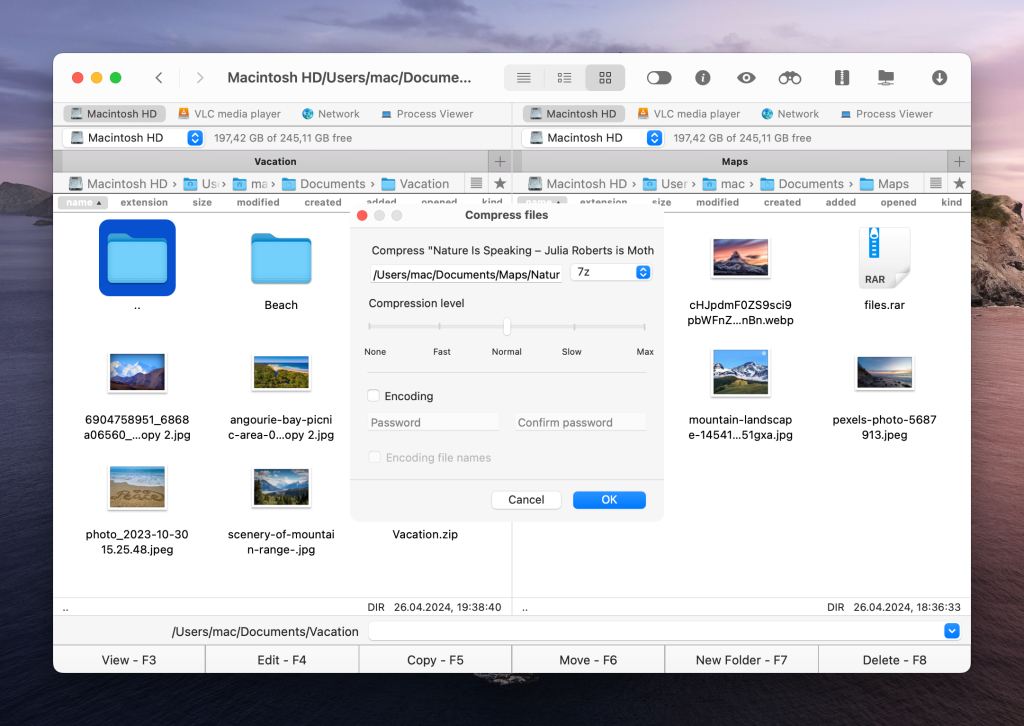
Open Commander One and choose the folder or file you want to reduce in size.
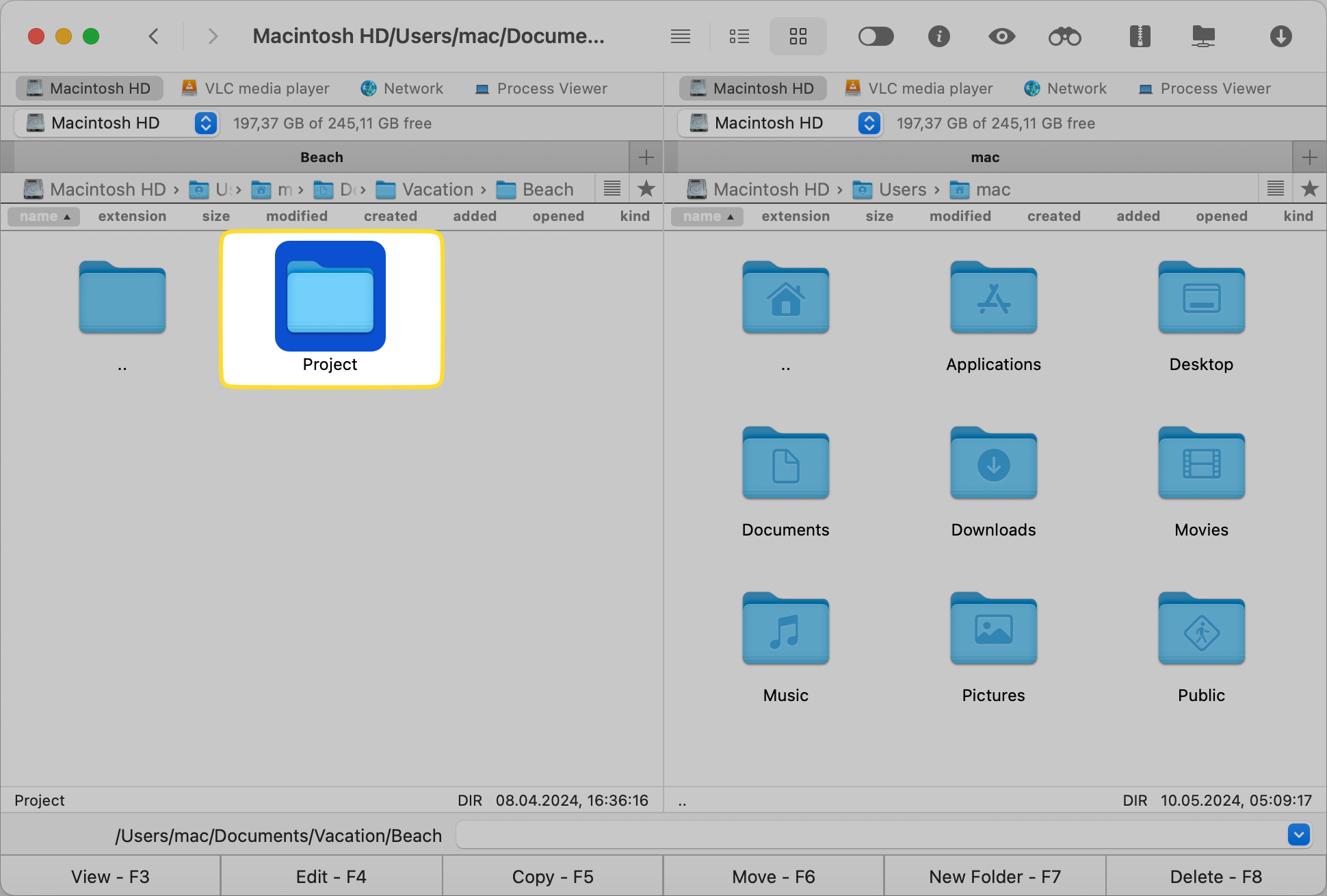
Click on the Archive icon at the top, select the desired archive format, and adjust settings as needed.
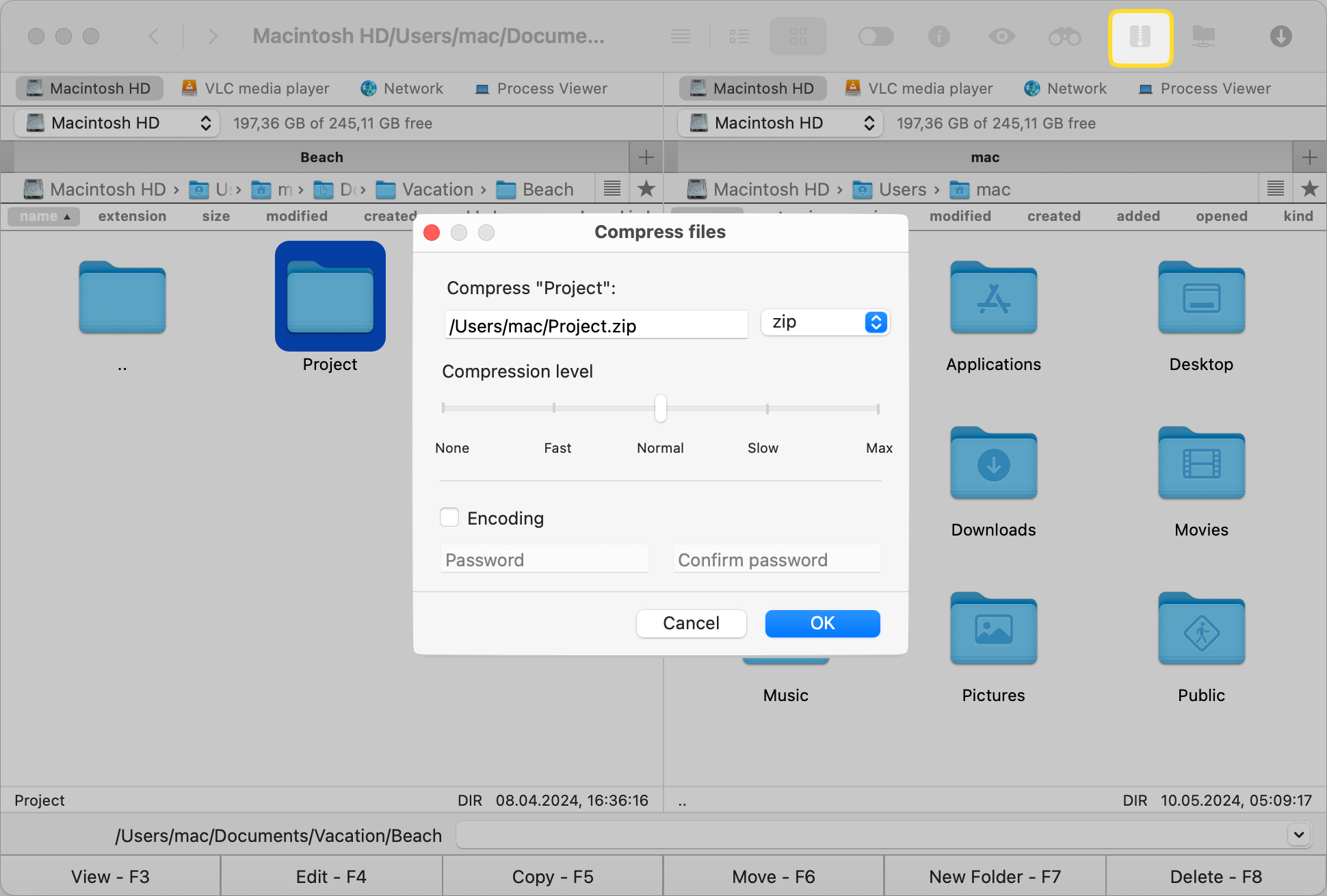
The compressed file will be displayed in the target pane.
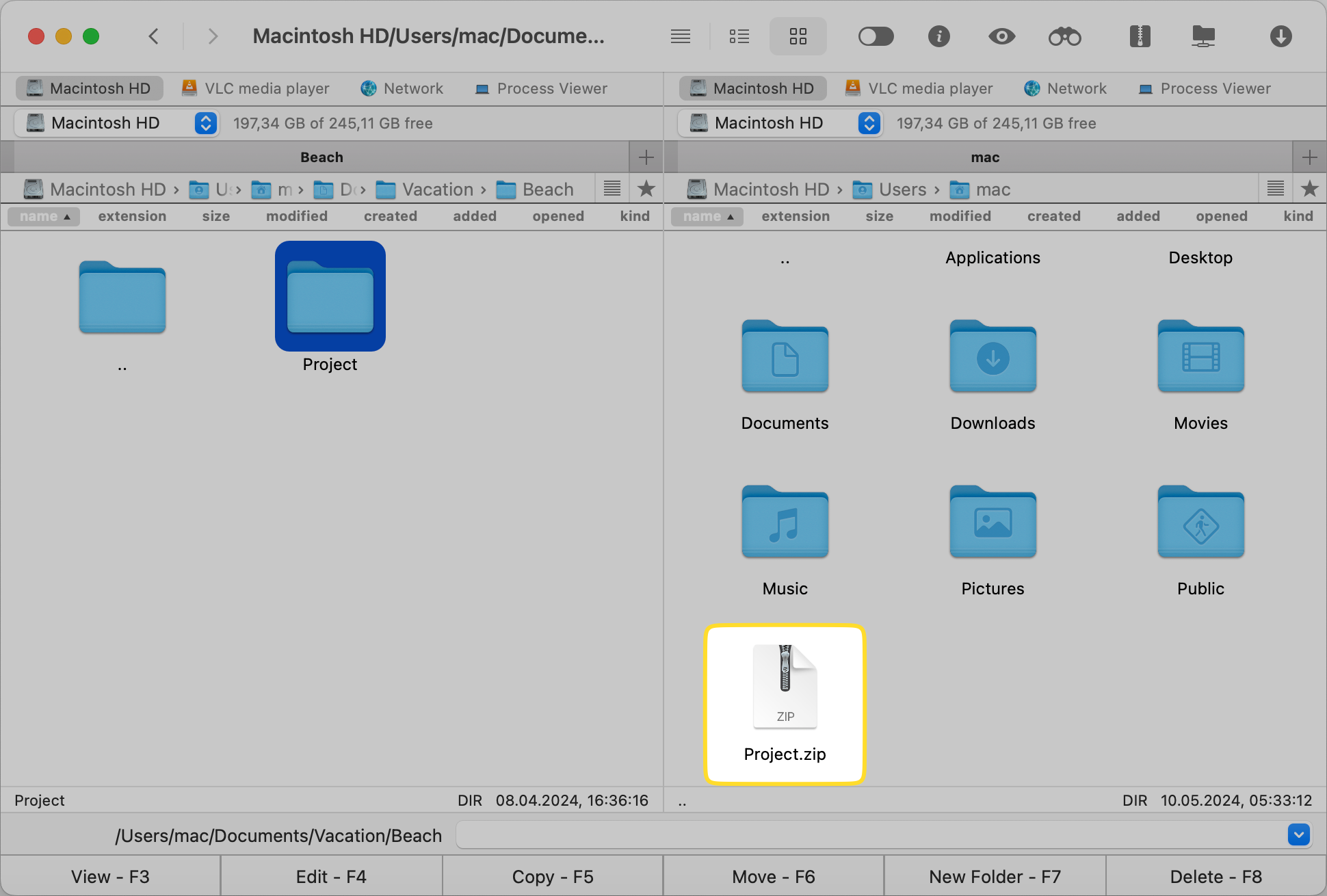
You can now send your archived file via email or upload it to your cloud storage.
Transfer big files using FTP/SFTP
FTP, or File Transfer Protocol, is a network protocol designed for moving files between a server and a client via the Internet. It is one of the efficient ways for sharing big files, but still, it lacks security. Alternatively, FTPS and SFTP offer enhanced security through SSL/TLS encryption and secure shell encryption, respectively, ensuring secure large file transfers.
To send files using this method, make sure the server is properly configured and you have the necessary credentials to access it. Additionally, you’ll need to install an FTP/SFTP client on your computer. Depending on your operating system, you have several options available, such as Cyberduck, FileZilla, Commander One, etc. Once installed, users can easily select files for transfer using an intuitive interface, simply by clicking and dragging them into place.
Use FTP with Commander One
Commander One is a powerful FTP/SFTP client for Mac. Its intuitive interface greatly streamlines file management tasks. With Commander One, you can effortlessly connect to FTP, SFTP or WebDAV and work with files and folders stored on remote servers as with any other folder on your Mac – copy, edit, delete, upload and download files to/from the server, and more. Besides, Commander One offers full support for popular cloud storage platforms, meaning you can also access and manage your cloud files within the app.
FTP Server Alternatives (Cloud Storages/Drives)
Security is paramount when working with sensitive data. Remember to consider the following points before transferring:
- Encrypt sensitive files to prevent unauthorized access.
- Opt for services offering end-to-end encryption for heightened security during transfers.
- Keep passwords updated and use two-factor authentication whenever possible.
- Review third-party services’ privacy policies to understand how your data will be managed.
Send big files using cloud storages
Cloud storage services offer an excellent solution for file transfers. The sender can upload large files to the cloud and share the link with other users. After receiving the URL, the recipient can access and download the files from any internet-connected device.
This method works seamlessly on both smartphones and computers thanks to automatic syncing on most cloud platforms. However, it’s worth noting that recipients must be registered with the cloud service you’re using to access the files. What’s more, some platforms offer additional features like password protection or setting the expiration date for a shared link.

Google Drive, Dropbox and OneDrive are among the most popular storages. For example, Google Drive provides free file storage of up to 15 GB for users with a Gmail account. It supports various file types and allows easy sharing via links, facilitating collaborative work.

Google Drive
Google Drive is a cloud storage service that seamlessly integrates with Google Workspace apps such as Docs, Sheets, and Slides. It provides 15 GB of free storage shared across Drive, Gmail, and Google Photos, with paid Google One plans offering up to 2 TB of space.
Google Drive lets you store, sync, and share files across devices, collaborate on documents in real time, and take advantage of AI-powered features. Files can be shared with flexible permission settings, edited offline, and accessed via web, desktop, and mobile apps.
How to send large files with Google Drive
- Go to drive.google.com and sign in to your Google account. Click New → File upload, then select the files you want to send, or simply drag and drop them directly into Google Drive.
- Once the upload is complete, right-click the file and select Share. Enter the recipients’ email addresses to send an invitation, or copy the generated link to share it via email or messaging apps.
- Set the appropriate access permissions: Viewer, Commenter, Editor.
You can also allow Anyone with the link to access the file.
Dropbox
Dropbox is a widely used cloud storage and collaboration service that allows users to sync files across devices, share them securely with AES-256 encryption, and collaborate in real time. It integrates seamlessly with Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace, making teamwork more efficient.
Dropbox supports both personal and business use and works across desktop and mobile platforms. Advanced plans offer scalable storage, enhanced security, and administrative controls for managing users and data.
Sending files using Dropbox
- Go to dropbox.com, sign in to your account, and navigate to More → Transfer → Create transfer.
- Add files by dragging them from your computer or selecting Add from Dropbox.
- Click the gear icon to set a password and choose an expiration date.
- Click Create transfer to generate your transfer.
- Share your files by clicking Send email to enter recipients’ email addresses, or select Copy link to share the transfer link manually.
- Send big files: You can share files up to 2 TB using the Dropbox desktop app.
- Keep files safe: Protect your transfers with passwords, set expiration dates, and get download notifications.
- No account needed: Recipients can access files with a shared link, even without a Dropbox account.
OneDrive
OneDrive is Microsoft’s cloud storage service that lets you securely store, access, and share files across devices. You can share files via links or email with customizable permissions. Integrated with Windows and Microsoft 365 apps like Word, Excel, and PowerPoint, it enables real-time collaboration and seamless syncing. Users get 5 GB of free storage, with paid plans offering up to 1 TB or more.
OneDrive supports automatic backup of photos and documents, version history, and advanced security features like ransomware detection and file encryption. Accessible via web, desktop, and mobile apps, it’s a reliable solution for personal and professional file management and cloud collaboration.
How to transfer large files via OneDrive
- Go to OneDrive and click Upload and select the file(s) or folder you want to share.
- Right-click the file or folder and select Share. Choose how you want to share:
• Email – Enter recipients’ email addresses.
• Link – Generate a link you can copy and send. - Decide if recipients can edit or view only.
Optional: Set an expiration date or password for extra security. - Click Send (if using email) or share the copied link through your preferred method (chat, messaging apps, etc.).
Manage cloud storages in one app
Managing files across multiple cloud storage services can indeed be a challenge. However, third-party software like Cyberduck, CloudMounter (for Windows), and Commander One (for macOS), make it easy by integrating with top online storage services, including Google Drive, Dropbox, OneDrive, Mega, Amazon S3, and more. With Commander One, you gain centralized access to all your clouds through a convenient dual-pane interface. Plus, you can add as many accounts as needed and work with your online files simultaneously.
Moreover, Commander One prioritizes the security of your data. With its built-in encryption feature, the app ensures that your files stored on any of your online connections are thoroughly protected against unauthorized access.
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve explored various methods to help you efficiently send large files, such as using cloud services, FTP/SFTP transfers, and compressing files beforehand. Each method comes with its own pros and cons, but they all contribute to improving workflow, productivity, and collaboration. Furthermore, third-apps like Commander One simplify the file-sharing process, offering security, a robust feature set, and a unified interface for a better user experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, Commander One allows for password protection of compressed files and folders on macOS.
Most cloud storage services have limits on the size of files you can upload. These limits vary depending on the provider and your account type.